How to run Spring Boot and MongoDB in Docker container
Introduction
This tutorial describes how to run Spring Boot application and Mongo DB in Docker containers.
For a demo purposes we’ll use the following project: spring-mongo-demo. All sources can be found on Github.
Our goal is to run our Spring Boot application and MongoDB in its own containers.
Some words about Demo project
Demo project (spring-boot-demo) is very simple and does the following: it saves the users into Mongo DB. A new added user is displayed in the Users table on the bottom of the page:
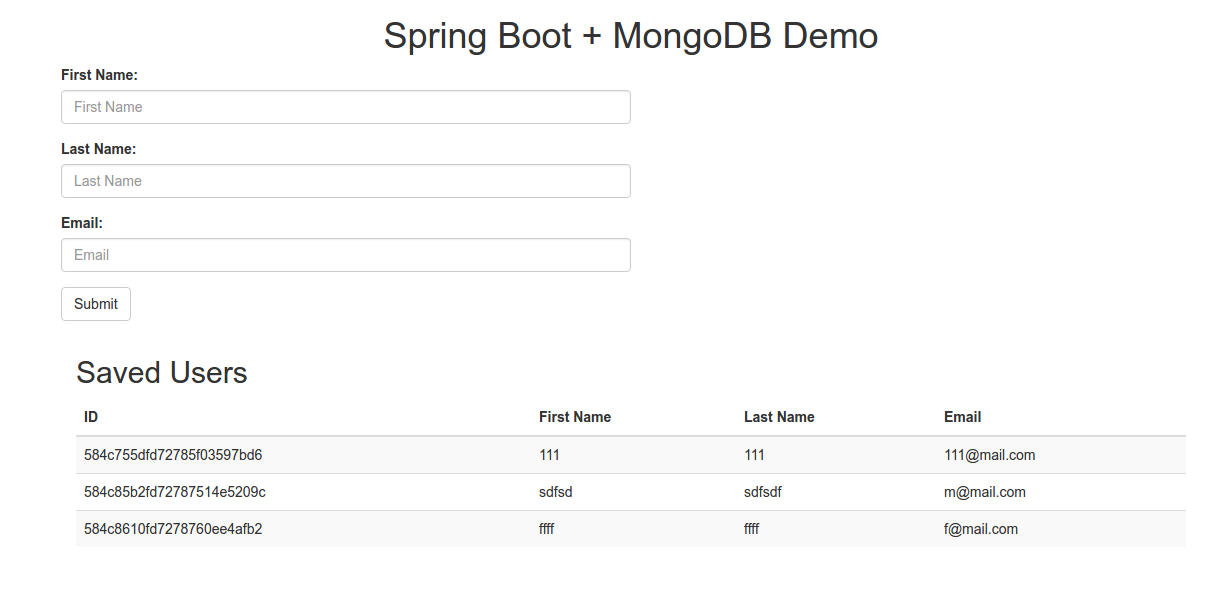
Requirements
We need:
- Ubuntu 16.04 or other Linux distribution
- Docker
- Java JDK
First of all Docker should be already installed. How to install Docker I described into the following tutorial : How to install Docker on Ubuntu 16.04
How to install Oracle JDK could be found here: INSTALL ORACLE JAVA 8 IN UBUNTU OR LINUX MINT VIA PPA REPOSITORY [JDK8]
How to run in Docker
As was mentioned above we need 2 containers: the first container will be used to run our Java application. The second container will be used to run MongoDB.
Create Docker Network
Our 2 containers should communicate with each other. To do so we need to create a new docker Network named spring_demo_net:
docker network create spring_demo_net
On the start our containers will connect to this network.
How to run MongoDB in Docker.
For MongoDB we’ll use the official image from Docker Hub.
Before starting the MongoDB container we need to create a folder where Mongo will store all the data:
mkdir -p ~/mongo-data
Now Let’s start the Mongo container into the following way:
docker run --name spring-demo-mongo --network=spring_demo_net -v /home/ubuntu/mongo-data:/data/db -d mongo
docker runstarts the container--name spring-demo-mongospecifies the name of the container.--network=spring_demo_netmeans to which network container should be connected-v /home/ubuntu/mongo-data:/data/dbshares the host’s/home/ubuntu/mongo-datafolder and mounts it to the container’s/data/dbfolder.-dmeans to start the container as a daemon.mongois a docker image name.
To verify our Mongo container is running we can use the following command:
docker ps
The output will look into the following way:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
1b6ff814b73c mongo "/entrypoint.sh mongo" 4 seconds ago Up 3 seconds 27017/tcp spring-demo-mongo
How to run Spring Boot in Docker.
To run our Demo application we’ll use the official Oracle image for Open JDK. Actually we’ll build our own image upon the official openjdk Docker image.
Create Dockerfile
To build our own image we can use the following Dockerfile file:
FROM openjdk:8-jdk
ADD springboot-mongo-demo.jar springboot-mongo-demo.jar
RUN sh -c 'touch /springboot-mongo-demo.jar'
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-Dspring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://spring-demo-mongo/users","-Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom","-jar","/springboot-mongo-demo.jar"]
Dockerfile contains steps for building our image.
FROM openjdk:8-jdk- means to build our image uponopenjdkimage from Docker Hub.ADD springboot-mongo-demo.jar springboot-mongo-demo.jar- adds our applicationspringboot-mongo-demo.jarfile to the container.RUN sh -c 'touch /springboot-mongo-demo.jar'- runs addedjarfile inside the container.ENTRYPOINT ....- adds (ENTRYPOINT) the configuration for running ourjarfile.
I’d like to pay your attention on the following Entrypoint’s parameter:-Dspring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://spring-demo-mongo/users. This parameter specifies URI forMongoDB. So, we can create different images for different environment, e.g. for QA and PROD with different URI.
And alsospring-demo-mongoshould be the same as named ourMongoDBcontainer.
Dockerfile could be placed at any folder. For demo purpose we’ve placed Dockerfile into springboot-mongo-demo/docker/ folder of our project.
Build Java project
We are almost ready to build our image, but first we need to build our Java project and place the jar file into the springboot-mongo-demo/docker folder of our project:
./gradlew clean build && cp build/libs/springboot-mongo-demo.jar docker/
Build Docker image
Now let’s build docker image. Change the directory to springboot-mongo-demo/docker and run the following command:
docker build --tag=spring-demo-1.0 .
--tag=spring-demo-1.0 - specifies the name of our container. It can be used for starting, stopping, restarting, removing container in easier way.
The output will look like this:
Step 1 : FROM openjdk:8-jdk
---> 861e95c114d6
Step 2 : MAINTAINER Aliaksei Bahdanau [email protected]
---> Using cache
---> 0069240de54a
Step 3 : ADD springboot-mongo-demo.jar springboot-mongo-demo.jar
---> f689c6b5d60c
Removing intermediate container 8c1b8536fd37
Step 4 : RUN sh -c 'touch /springboot-mongo-demo.jar'
---> Running in 04e627b54b98
---> 69b94c770ad5
Removing intermediate container 04e627b54b98
Step 5 : ENTRYPOINT java -Dspring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://spring-demo-mongo/users -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom -jar /springboot-mongo-demo.jar
---> Running in 0135836ed1bf
---> c78a5f6516d3
Removing intermediate container 0135836ed1bf
Successfully built c78a5f6516d3
Now we can verify that our spring-demo-1.0 image is available locally:
docker images
The output will look like:
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
spring-demo-1.0 latest c78a5f6516d3 3 minutes ago 679.5 MB
openjdk 8-jdk 861e95c114d6 20 minutes ago 643.2 MB
mongo latest 7f09d45df511 20 minutes ago 336.1 MB
Run Docker container
If our spring-demo-1.0 image was build successfully and available locally, we can run container with our Spring Boot application as follows:
docker run -d --name spring-demo --network=spring_demo_net -p 8080:8080 spring-demo-1.0
The command for running Spring Boot application inside docker looks very similar as for starting MongoDB container but with the following difference:
-p 8080:8080 - publishes a container’s port(s) to the host.
To see containers log file we can use the following command:
docker logs spring-demo
Additional resource